CRM Software Cost: 7 Shocking Truths You Must Know in 2024
Thinking about CRM software cost? You’re not alone. Thousands of businesses are trying to figure out how much they should really pay—and what they’re actually getting. Let’s break it down, no fluff, just facts.
CRM Software Cost: The Real Numbers in 2024

When it comes to CRM software cost, the numbers vary wildly depending on your business size, industry, and specific needs. But understanding the baseline pricing models is the first step to making a smart investment. According to Gartner, the global CRM market is projected to exceed $80 billion by 2025, showing just how critical these tools have become.
Monthly vs. Annual Pricing Models
Most CRM platforms offer both monthly and annual billing options. While monthly plans provide flexibility, annual subscriptions often come with a 10–20% discount. For example, HubSpot CRM offers a free tier, but its Sales Hub starts at $18/month/user when billed monthly, and drops to $14.40/month/user when billed annually.
- Monthly billing: Ideal for startups testing the waters.
- Annual billing: Better value for established teams with stable user counts.
- Some vendors offer quarterly plans as a middle ground.
“The shift from CapEx to OpEx in CRM spending has made it easier for SMBs to adopt enterprise-grade tools.” — Gartner Research, 2023
Free vs. Paid CRM: What’s the Catch?
Yes, free CRM software exists—like HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, and Bitrix24. But they come with limitations. Free versions typically cap features such as automation, reporting, and user numbers. For instance, Zoho CRM’s free plan supports up to 3 users and basic contact management, but lacks advanced sales forecasting.
- Free CRMs are great for solopreneurs or very small teams.
- Hidden costs include integration fees, training, and data migration.
- Scaling often means upgrading, which can spike CRM software cost unexpectedly.
Factors That Influence CRM Software Cost
CRM pricing isn’t one-size-fits-all. Several variables affect how much you’ll pay. Understanding these can help you avoid overpaying or under-equipping your team.
Number of Users and Licensing
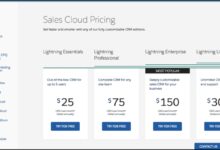
Most CRM systems use a per-user, per-month pricing model. Salesforce, for example, starts at $25/user/month for its Essentials plan and goes up to $300/user/month for Unlimited. The more users, the higher the total CRM software cost—even if not all users need full access.
- Some vendors offer team-based pricing instead of per-user.
- Consider role-based licensing: not every employee needs admin rights.
- Over-licensing is a common budget killer.
Feature Tiers and Module Add-Ons
Vendors segment their offerings into tiers: Free, Starter, Professional, Enterprise. Each tier unlocks more features. Marketing automation, AI insights, and advanced analytics often live in higher tiers. Additionally, modules like customer service, e-commerce integration, or telephony can be add-ons with separate fees.
- HubSpot charges extra for tools like Conversations and Service Hub.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 bundles CRM and ERP, but modules are sold separately.
- Always audit which features you actually need.
Deployment Type: Cloud vs. On-Premise
Cloud-based CRMs (SaaS) dominate the market due to lower upfront costs and easier maintenance. On-premise solutions, while rare today, still exist for industries with strict data compliance needs (e.g., government, finance). However, on-premise CRM software cost includes server hardware, IT staff, and ongoing maintenance—often totaling tens of thousands upfront.
- Cloud CRM: Predictable monthly fees, automatic updates.
- On-premise: High CapEx, long-term control, but complex to manage.
- Hybrid models are emerging but niche.
Hidden Costs Behind CRM Software Cost
The sticker price is just the beginning. Many businesses underestimate the total cost of ownership (TCO) when adopting a CRM. A study by Nucleus Research found that implementation and training can double the initial CRM software cost over three years.
Implementation and Setup Fees
Even cloud CRMs require setup: data migration, user onboarding, workflow configuration. Some vendors charge flat setup fees ($500–$5,000), while others offer free onboarding for basic plans. Salesforce, for example, recommends using a certified partner for implementation, which can cost $10,000+ for mid-sized companies.
- DIY setup saves money but risks poor adoption.
- Professional services ensure smooth integration but add cost.
- Ask vendors: Is setup included? Are there tiered support options?
Integration and API Costs
Your CRM doesn’t work in isolation. It needs to connect with email, marketing tools, ERP, and e-commerce platforms. While basic integrations (like Gmail or Outlook) are often free, custom API usage or third-party connectors (via Zapier or MuleSoft) can incur fees.
- Zapier charges based on tasks and speed—$20–$100+/month.
- Some CRMs limit API calls in lower tiers.
- Custom API development can cost $5,000–$20,000.
Training and User Adoption
A CRM is only as good as its users. Poor training leads to low adoption, rendering the system useless. Training costs vary: self-paced videos (free), live webinars ($500–$2,000), or on-site coaching ($5,000+). According to Salesforce, companies that invest in training see 3x higher ROI.
- Allocate 10–15% of your CRM software cost budget for training.
- Use gamification and internal champions to boost adoption.
- Track login rates and data entry completeness post-launch.
Top CRM Platforms and Their Real-World Pricing
Let’s look at how CRM software cost breaks down across leading platforms. This comparison helps you benchmark what’s reasonable for your business.
Salesforce: Enterprise Power at a Premium
Salesforce is the market leader, but it’s also one of the most expensive. Its CRM software cost starts at $25/user/month for Essentials and climbs to $300/user/month for Unlimited. Add-ons like Einstein AI or Pardot (marketing automation) can push costs over $500/user/month.
- Best for: Large enterprises with complex sales cycles.
- Pros: Highly customizable, vast app ecosystem (AppExchange).
- Cons: Steep learning curve, high total cost with add-ons.
“Salesforce isn’t just a CRM—it’s a platform. That power comes at a price.” — TechRadar, 2023
HubSpot: Scalable for SMBs and Mid-Market
HubSpot offers a freemium model that’s attractive to small businesses. The CRM is free forever, but Sales Hub starts at $18/month/user. Marketing Hub begins at $18/month (billed annually), and Service Hub at $23/month. Full suite bundles can reach $800+/month for 10 users.
- Best for: Growing companies focused on inbound marketing.
- Pros: User-friendly, excellent onboarding, free tools.
- Cons: Costs rise quickly with add-ons; limited customization at scale.
Zoho CRM: Budget-Friendly with Depth
Zoho CRM is known for affordability. The free plan supports 3 users. The Standard plan is $14/user/month, Professional is $23, and Enterprise is $40. It includes AI (Zia), automation, and multichannel support even in mid-tiers.
- Best for: Small to mid-sized businesses on a budget.
- Pros: Feature-rich at low cost, strong automation.
- Cons: Interface feels dated; support can be slow.
How to Reduce CRM Software Cost Without Sacrificing Value
You don’t need to spend a fortune to get a powerful CRM. Smart strategies can cut CRM software cost by 30–50% while maintaining functionality.
Negotiate with Vendors and Resellers
Most CRM vendors expect negotiation, especially for annual contracts or 10+ users. Resellers often offer discounts to meet quotas. For example, a Microsoft Dynamics 365 reseller might offer 15% off list price for a 12-month commitment.
- Ask for bundled pricing across modules.
- Request free training or extended trials.
- Leverage competitor quotes as leverage.
Start Small and Scale Gradually
Don’t buy the Enterprise plan on day one. Start with a basic tier and upgrade as you grow. Use the free version to test workflows, then move to paid only when you hit user or feature limits.
- Example: Begin with HubSpot’s free CRM, add Sales Hub when you need email tracking.
- Monitor usage metrics before upgrading.
- Avoid over-provisioning early.
Use Open Source or Low-Code Alternatives
For tech-savvy teams, open-source CRMs like SuiteCRM or EspoCRM offer full control at low cost. They’re free to download, but require in-house IT for setup and maintenance. Low-code platforms like Zoho Creator let you build custom CRMs affordably.
- Pros: No licensing fees, highly customizable.
- Cons: Higher technical barrier, no official support.
- Best for: Companies with internal development resources.
ROI of CRM: Is the Cost Worth It?
The real question isn’t just how much CRM software costs—but what return you get. According to Nucleus Research, the average ROI for CRM is $8.71 for every $1 spent. But that depends on proper implementation and usage.
Measuring CRM Success with KPIs
To justify CRM software cost, track key performance indicators (KPIs) before and after implementation. Common metrics include:
- Sales cycle length: Did it shorten?
- Lead conversion rate: Did it improve?
- Customer retention: Did churn decrease?
- Team productivity: Are reps spending less time on admin?
“CRM isn’t a cost center—it’s a revenue accelerator when used right.” — Forbes
Case Study: How a Mid-Sized Company Saved $50K Annually
A B2B services firm with 50 employees switched from a legacy on-premise CRM to Zoho CRM. Their old system cost $70,000/year in maintenance, licenses, and IT support. The new cloud-based Zoho setup cost $24,000/year (including training and integration). Within 8 months, they reduced lead response time by 60% and increased sales by 22%.
- Initial CRM software cost: $24,000/year vs. $70,000.
- Savings: $46,000/year.
- Revenue impact: +$150,000 in new deals attributed to better lead tracking.
Future Trends Affecting CRM Software Cost
The CRM landscape is evolving fast. AI, automation, and vertical-specific solutions are reshaping pricing models and value propositions.
AI and Automation: Premium Features or Standard?
AI-powered insights (like lead scoring, sentiment analysis, and forecasting) were once premium add-ons. Now, platforms like Salesforce Einstein and HubSpot AI are bundling them into mid-tier plans. Expect AI to become standard—but vendors may raise base prices to cover R&D.
- Today: AI often costs extra (e.g., $50/user/month).
- 2025 Forecast: AI included in Professional tiers, but base price increases 10–15%.
- Long-term: AI could reduce labor costs, offsetting software price hikes.
Industry-Specific CRMs: Higher Cost, Higher Value
Generic CRMs are being replaced by vertical solutions—like Veeva for life sciences or Realtor CRM for real estate. These are often more expensive but deliver faster ROI due to pre-built workflows and compliance features.
- Example: Salesforce Health Cloud costs $300/user/month but meets HIPAA requirements out of the box.
- Value: Reduced customization time, faster deployment.
- Trade-off: Less flexibility for non-core use cases.
Subscription Fatigue and Bundling
As businesses use more SaaS tools, subscription fatigue is real. Vendors are responding with bundled suites (e.g., Microsoft 365 + Dynamics, Zoho One). These can reduce CRM software cost by offering discounts for multi-product adoption.
- Zoho One includes CRM, email, finance, and HR for $37/user/month.
- Microsoft bundles Dynamics 365 with Office 365 for enterprise clients.
- Bundling simplifies billing but may include unused tools.
What is the average CRM software cost per user?
The average CRM software cost ranges from $12 to $100 per user per month. Basic plans (like Zoho Standard or HubSpot Starter) start at $12–$18, while enterprise solutions (Salesforce Unlimited, Microsoft Dynamics) can exceed $200/user/month when fully configured.
Are there any truly free CRM software options?
Yes, several CRMs offer free plans with core features. HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, and Bitrix24 provide free tiers for up to 1–3 users. These are ideal for solopreneurs or startups but lack advanced automation, reporting, and integrations available in paid versions.
How can I reduce my CRM software cost?
You can reduce CRM software cost by negotiating annual contracts, starting with a lower-tier plan, leveraging free trials, using open-source alternatives, or bundling with other software. Also, avoid over-licensing and invest in training to maximize ROI.
Does CRM software cost include implementation?
Not always. Many vendors charge separately for setup, data migration, and training. Cloud CRMs often include basic onboarding, but complex implementations (especially for Salesforce or Dynamics) may require third-party consultants, adding thousands to the total cost.
Which CRM offers the best value for small businesses?
Zoho CRM and HubSpot CRM are widely regarded as the best value for small businesses. Both offer robust free plans, affordable paid tiers, and scalable features. Zoho is more budget-focused, while HubSpot excels in marketing and user experience.
CRM software cost isn’t just about the monthly subscription. It’s a blend of licensing, implementation, training, and hidden fees. The smartest buyers don’t look for the cheapest option—they look for the best value. Whether you choose Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho, or an open-source solution, the key is aligning cost with your business goals. By understanding pricing models, avoiding hidden costs, and measuring ROI, you can turn your CRM from a cost center into a growth engine. The future of CRM is smarter, more integrated, and more valuable—but only if you invest wisely.
Further Reading: